Anemia is a prevalent medical condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, leading to a reduced ability of the blood to carry oxygen to body tissues. It affects millions of people worldwide, impacting their overall health and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for anemia is crucial in managing and preventing this condition. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of anemia, including its causes, symptoms, natural remedies, and medical treatments.
I. Causes of Anemia:
Anemia can be caused by various factors, and understanding these underlying causes is vital in determining the appropriate treatment. Some common causes include:

- Iron Deficiency:
The most prevalent cause of anemia, iron deficiency occurs when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce hemoglobin. This can be due to poor dietary intake, malabsorption issues, or increased iron requirements during pregnancy or growth periods.
- Vitamin Deficiencies:
Anemia can result from deficiencies in vitamin B12 or folic acid, both of which are essential for red blood cell production. Individuals with a poor diet or certain medical conditions may be prone to this type of anemia.
- Chronic Diseases:
Certain chronic conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, inflammatory disorders, or autoimmune diseases, can disrupt red blood cell production or lifespan, leading to anemia.
- Hemolytic Anemia:
This type of anemia occurs when red blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can produce them. It can be inherited or acquired and may result from various factors, including autoimmune disorders and infections.
- Hemorrhage:
Excessive bleeding, whether due to trauma, ulcers, or heavy menstruation, can cause anemia by reducing the overall volume of blood and red blood cells in the body.
II. Symptoms of Anemia:
Recognizing the symptoms of is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. The symptoms can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Common symptoms include:
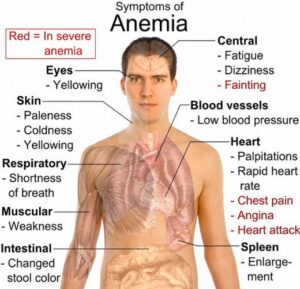
- Fatigue and Weakness:
Anemic individuals often experience persistent tiredness and a lack of energy, even with adequate rest.
- Pale Skin and Mucous Membranes:
A reduced number of red blood cells can result in paleness of the skin and the mucous membranes inside the mouth and eyelids.
- Shortness of Breath:
As the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity diminishes, individuals may feel breathless even with mild physical exertion.
- Dizziness and Headaches:
Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain can lead to dizziness and frequent headaches.
- Cold Hands and Feet:
Anemia can cause poor circulation, leading to cold and clammy extremities
- Irregular Heartbeat:
In severe cases, anemia may cause the heart to work harder, resulting in an irregular or rapid heartbeat.
III. Natural Remedies for Anemia:
While medical treatments are essential for severe cases of anemia, mild cases or preventive measures can often be supported by natural remedies. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before trying any of these remedies:
- Dietary Changes:
Consuming iron-rich foods such as leafy greens, beans, lentils, nuts, and fortified cereals can help combat iron-deficiency anemia.
- Vitamin Supplements:
Taking vitamin B12 and folic acid supplements, when prescribed by a healthcare provider, can aid in addressing deficiencies.
- Herbal Remedies:
Certain herbs, such as nettle, dandelion root, and yellow dock, are believed to boost iron absorption and may be beneficial in mild cases of anemia.
- Vitamin C Intake:
Consuming foods rich in vitamin C, like citrus fruits and berries, can enhance iron absorption from plant-based sources.
- Avoidance of Iron Blockers:
Some foods and beverages, such as coffee, tea, and calcium-rich products, can hinder iron absorption and should be consumed in moderation.
IV. Medical Treatments for Anemia:
For more severe cases of anemia or when natural remedies are insufficient, medical interventions may be necessary. The appropriate treatment will depend on the specific type and cause of anemia:
- Iron Supplements:
In cases of iron-deficiency anemia, doctors may prescribe iron supplements in the form of pills, capsules, or intravenous infusions.
- Vitamin Injections:
For hyponemia resulting from vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency, vitamin injections may be administered to boost red blood cell production.
- Blood Transfusions:
In severe hyponemia or situations with significant blood loss, blood transfusions may be required to replenish red blood cells.
- Erythropoietin Injections:
Erythropoietin is a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells and may be used in certain cases of hyponemia.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions:
For hyponemia caused by chronic diseases or other underlying conditions, addressing the root cause is essential in managing the anemia effectively.

Conclusion:
hyponemiais a widespread medical condition that can significantly impact a person’s well-being and daily life. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the various causes are crucial in seeking timely diagnosis and treatment. While natural remedies may be beneficial for mild cases or as preventive measures, medical treatments play a pivotal role in managing severe hyponemia. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans to ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals affected by hyponemia. With appropriate care and attention, individuals can effectively manage hyponemia and improve their overall quality of life.